
What is the relationship between stock markets and foreign exchange markets?
Understanding economic trends is key for anyone with exposure to currency risk. Being able to spot trends and potential movement in a currency can help with mitigating risk.
There are many ways economists gain insight into foreign exchange markets, such as looking at economic reports and gross domestic product (GDP). In this article, we explain how and why changes in stock markets impact the pound directly, as well as why foreign exchange investors keep a close eye on stock markets.
You might assume that the correlation between foreign exchange markets and stock markets would always be positive. In other words that a rising UK stock market would mean a rising pound, and vice versa. After all, both indicate the general health of the economy. However, there are times when it can be negative, moving in opposite directions.
Exchange rates and profitability
Not only that, but each can impact the other directly. Sterling’s strength or weakness has been one of the strongest drivers in the performance of the FTSE 100 stock index. After all, many of the companies listed in the FTSE operate internationally and transact in multiple currencies (including GBP), so the exchange rate can have a direct and powerful impact on profitability.
For example, if GBP/USD strengthens, dollar revenues are worth less and profits are lower. Hence the, the correlation is very often a negative pattern.
This is what happened before, during and after the UK’s Brexit deal was announced. As GBP rose against USD, FTSE100 stocks simultaneously fell.
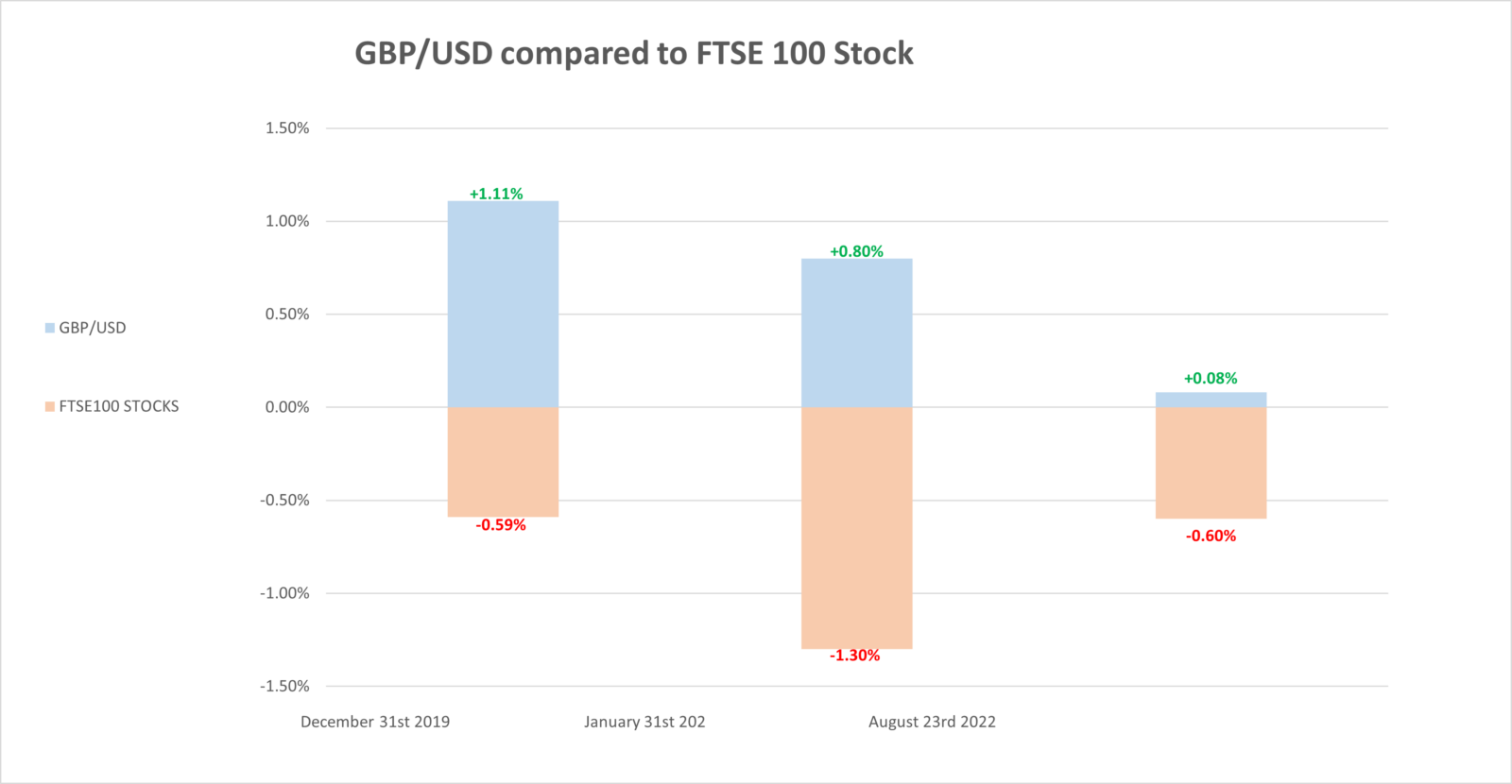
This graph shows the GBP/USD currency rate increase compared to FTSE 100 stocks decrease (measured before, during and after the UK’s Brexit deal)
Supply and demand
When a country’s stock market rises, this gives investors confidence that the country’s economy is also rising. As a result, this leads to increased interest from foreign investors and a demand for the domestic currency. Likewise, if a country’s stock market underperforms then that confidence and demand lowers as investors will be less likely to spend funds.
For example, if the UK’s stock market rose and investors demanded more British pound sterling, the pound would strengthen against other currencies. Likewise, if there was an excess supply of GBP, sterling would weaken relative to those other currencies.
Politics and the markets
Government policy has a huge impact on foreign exchange market, and stocks too. For example, in the UK, after Boris Johnson announced his resignation, UK stocks rose and the pound climbed.
Another example is Brexit. When the UK decided to leave the European Union in 2016, sterling dropped immediately. The pound’s swift decline, however, increased the share prices of larger, globally-operating UK-listed companies. As the picture of Brexit became clearer, many companies saw share prices eventually decline.
Once the government struck the Brexit deal with the EU at the end of December 2020, the FTSE 100 index climbed 160 points (nearly 2.5%) – which was the highest it had reached since early March that year. Even so, the pound has never come close to regaining its former status.
Although currency markets are affected by many factors, understanding the relationship between the stock market and the currency market in particular, is a good place for businesses to start. This is because knowing what may cause a currency’s rate to fluctuate in the first place, can provide a key insight into how and when to mitigate (hedge) against the risk of fluctuating currencies.
With the current economic concerns around recession and its knock on effect on currency rates, it is vital to make sure your business mitigates (hedges) against those risks. Learn more about hedging services by visiting Currency Exchange Hedging Strategies, or get in touch to learn about Smart Hedge.

 020 7898 0500
020 7898 0500